“The Mirror Maze: Exploring the Impact of Body Dysmorphia on Self-Image”
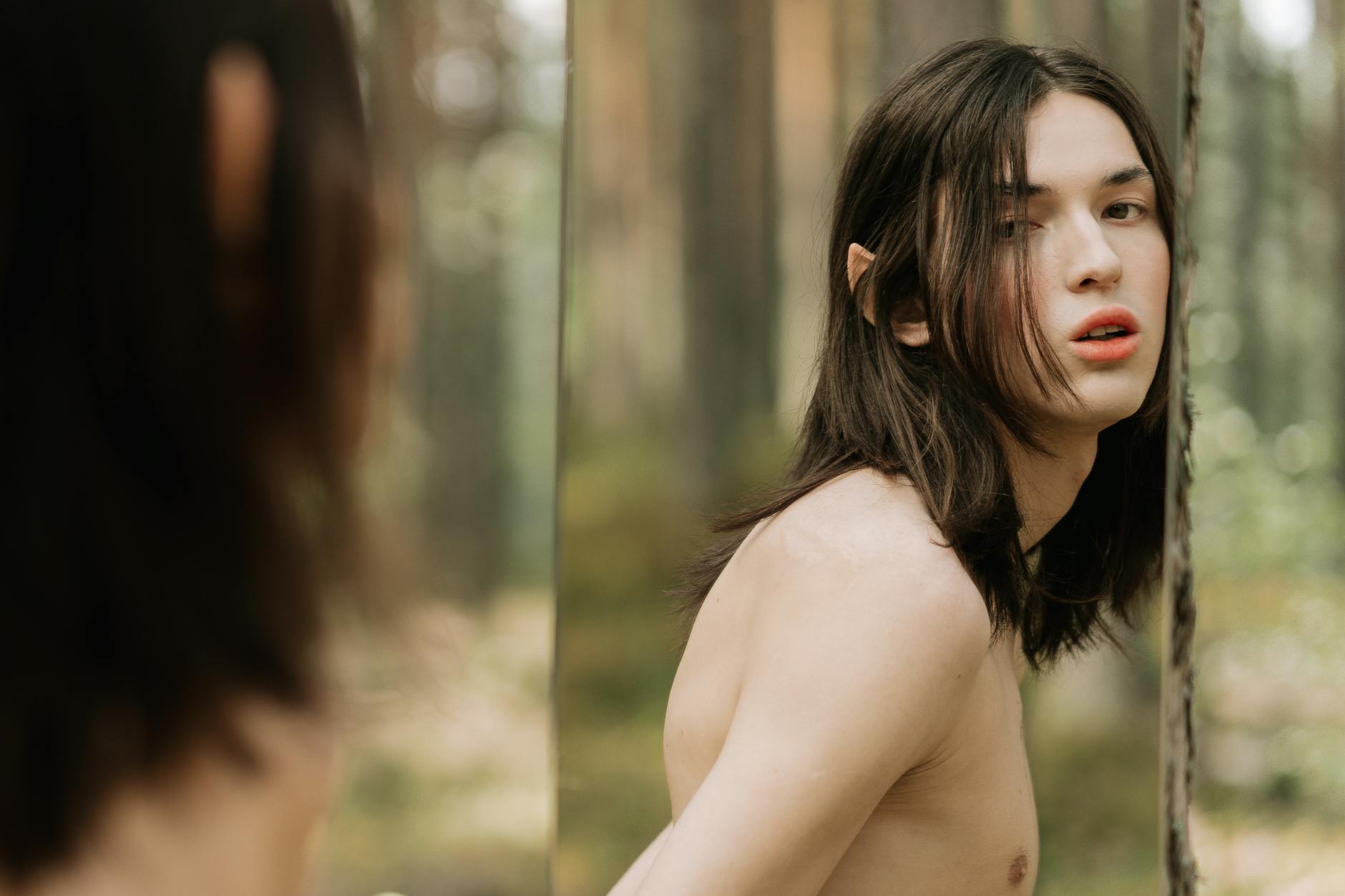 Image courtesy of cottonbro studio via Pexels
Image courtesy of cottonbro studio via Pexels
Have you ever spent hours examining yourself in the mirror, fixating on perceived flaws that others fail to notice? Have you constantly sought reassurance from friends and family, hoping they would dispel your insecurities? If so, you might be experiencing body dysmorphic disorder, commonly known as body dysmorphia.
Body dysmorphia is a mental health disorder characterized by a distorted perception of one’s appearance. Individuals with this condition obsessively focus on specific aspects of their body they perceive as flawed, despite the lack of any significant defects. These perceived imperfections become all-consuming, often causing significant distress and impairing various areas of life.
Understanding body dysmorphia is crucial in today’s image-obsessed society, as it affects countless individuals of all genders, ethnicities, and ages. By exploring this topic in a curated manner, we can shed light on the complexities of body dysmorphia and its profound impact on self-image.
Understanding Body Dysmorphia
To understand body dysmorphia, we must first delve into its definition and prevalence. Body dysmorphia is a mental health condition categorized within the obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) spectrum. Individuals with body dysmorphia engage in repetitive behaviours, such as checking mirrors, seeking reassurance, and excessive grooming, as a result of their distorted body image.
The disorder affects an estimated 1.7-2.4% of the population, but its prevalence is likely higher due to underreported cases. Body dysmorphia can develop in adolescence or early adulthood, impacting individuals during critical stages of identity formation and self-esteem development.
Various factors contribute to the development of body dysmorphia. While research suggests a genetic and biological predisposition, environmental and sociocultural influences play significant roles as well. Images perpetuated by media, societal pressure to conform to narrow beauty standards, and childhood experiences with bullying or body shaming can all contribute to the development of this disorder.
Symptoms and Effects of Body Dysmorphia.
There are several key symptoms that help identify body dysmorphia in individuals. Common signs include a preoccupation with perceived flaws to the extent that it interferes with daily functioning, significant distress caused by the perceived flaws, and frequent mirror checking or extensive grooming rituals.
The emotional and psychological impact of body dysmorphia is profound. Individuals with body dysmorphia often experience increased anxiety and depression, as well as a lowered sense of self-worth and body image dissatisfaction. These effects can be debilitating, leading to avoidance of social situations and a decreased quality of life.
“Embrace your true reflection, for beauty lies within the depths of self-acceptance. Discover the path to reclaiming self-image with this empowering blog post on understanding body dysmorphia. [insert link] #SelfLove #EmbraceYourReflection”
The Intersection of Media and Body Dysmorphia.
Media plays an influential role in shaping societal beauty standards, often leading to the perpetuation of body dysmorphia. The proliferation of digitally altered images in advertising and social media platforms creates unrealistic beauty ideals that are impossible for most individuals to attain.
Comparison culture exacerbates the effects of body dysmorphia. Constant exposure to seemingly “perfect” bodies in the media fosters feelings of inadequacy and self-criticism. It is essential to recognize the dangers of this culture and actively work towards dismantling its harmful impact.
Seeking and Providing Support for Body Dysmorphia.
Approaching individuals with body dysmorphia with empathy and understanding is crucial. Body dysmorphia is often misunderstood or trivialized, leading to further alienation and distress for those affected by the disorder. By destigmatizing mental health disorders and educating ourselves, we can promote compassion and support for individuals struggling with body dysmorphia.
Treatment options and resources are available for individuals with body dysmorphia. Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective evidence-based interventions, helping individuals challenge negative thoughts and behaviours associated with their body image. Support groups and online communities provide a safe space for individuals to share experiences, gain support, and learn coping strategies.
It is also important to acknowledge that body dysmorphia is a complex condition that often requires professional help. Seeking therapy or counselling from qualified mental health professionals can provide invaluable support and guidance on this challenging path.
Online support networks and communities can offer a sense of belonging and understanding. By connecting with individuals who share similar experiences, individuals with body dysmorphia can find solace, empathy, and mutual encouragement. These platforms provide a safe space for sharing struggles, triumphs, and insights, serving as a reminder that nobody is alone in their journey towards body positivity and mental well-being.
Promoting Body Positivity and Mental Well-being.
Embracing body positivity and prioritizing mental well-being are vital steps towards combating body dysmorphia. Society’s narrow definition of beauty needs to be challenged, and self-acceptance should be promoted as an alternative to unattainable perfection. By embracing diversity and celebrating individuality, we can foster a more inclusive and self-loving culture.
Media also plays a significant role in shaping our collective body perceptions. It is crucial to support brands and influencers who actively work towards promoting body positivity and realistic representations of diverse bodies. By advocating for a balanced media representation, we can contribute to healthier and more inclusive narratives surrounding beauty.
Conclusion.
Body dysmorphia is a complex disorder, intricately entangled with societal pressures and media influences. By understanding the nuances of body dysmorphia and its profound impact on self-image, we can actively contribute to a more compassionate and inclusive society. Let us remember that the way we perceive ourselves and others extends far beyond physical appearance. Together, we can challenge beauty norms, prioritize mental well-being, and curate a world where self-acceptance and self-love triumph.
In addition ,let us remember that beauty exists in every individual, regardless of their shape, size, or perceived flaws. Together, we can challenge societal beauty standards, foster acceptance, and create a world where lingerie is not just a garment but a symbol of empowerment for all.




















Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!